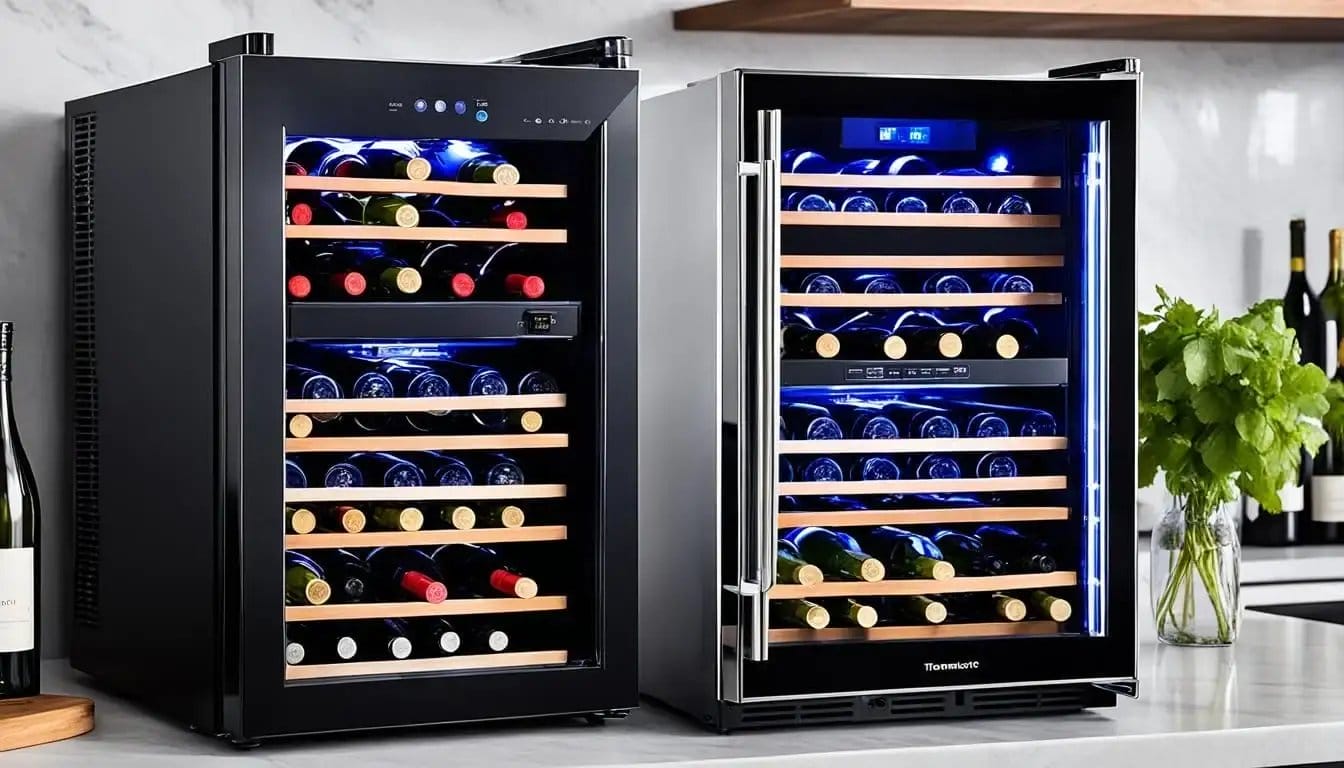
Choosing the right wine fridge can make all the difference. When deciding between a compressor or thermoelectric model, it’s essential to understand the differences in wine cooling technology.
In this guide, we will get into the world of wine fridges and explore the efficiency, performance, and features of compressor and thermoelectric wine coolers. Check further!
Key Takeaways:
- Compressor and thermoelectric wine coolers use different cooling technologies.
- Compressor coolers work similarly to traditional refrigerators, using a vapor compression cycle.
- Thermoelectric coolers operate based on the Peltier effect, creating a heat flux to cool the interior.
- Compressor coolers offer a wider temperature range, making them suitable for various wine types.
- Thermoelectric coolers are more energy-efficient and produce minimal noise and vibration.
How Compressor Wine Coolers Work
Compressor wine coolers operate using a vapor compression cycle, which is similar to the refrigeration process in standard refrigerators. This cycle relies on a coolant gas to remove heat from the interior of the wine cooler, keeping it at the desired temperature.
The major components of a compressor system include:
- The Compressor: The compressor is the heart of the system and is responsible for circulating and compressing the refrigerant gas.
- The Condenser: The condenser cools down the compressed gas, causing it to condense into a liquid form.
- The Expansion Valve: The expansion valve regulates the flow of the refrigerant into the evaporator.
- The Evaporator: The evaporator allows the liquid refrigerant to evaporate, absorbing heat from the interior of the wine cooler.
Once the refrigerant gas reaches the evaporator, it absorbs heat from the wine cooler’s interior, effectively cooling the contents of the cabinet.
- To distribute the cold air evenly, some compressor wine coolers incorporate fans that circulate the cold air throughout the entire cabinet.
- Compressor wine coolers offer powerful cooling capabilities and are suitable for storing a wide range of wines at precise temperatures.
- Their efficient vapor compression cycle ensures a consistent and reliable cooling performance, making them an excellent choice for wine enthusiasts looking to preserve the flavors and aromas of their favorite wines.
| Components | Function |
|---|---|
| Compressor | Circulates and compresses the refrigerant gas |
| Condenser | Cools down the compressed gas, causing it to condense into a liquid |
| Expansion Valve | Regulates the flow of the refrigerant into the evaporator |
| Evaporator | Allows the liquid refrigerant to evaporate, absorbing heat from the interior of the wine cooler |
How Thermoelectric Wine Coolers Work
Thermoelectric wine coolers operate based on the Peltier effect. By utilizing the Peltier effect and innovative cooling techniques, thermoelectric wine coolers provide reliable and efficient temperature control for wine storage.
- Electric currents are sent through two different metal sides, creating a heat flux. One side becomes hot, while the other becomes cold.
- The hot side is attached to a heat sink, which dissipates the heat into the air, while the cold side is placed inside the wine cooler.
- The absence of moving parts in thermoelectric coolers results in virtually no vibration. This eliminates the risk of disturbing the sediments in wine bottles, ensuring the preservation of flavor and aging processes.
- Some thermoelectric wine coolers also incorporate fans into their design, promoting better air circulation and enhancing cooling efficiency.

Temperature Range Comparison
With a clearer understanding of the temperature ranges of thermoelectric and compressor coolers, you can select the wine cooler that best suits your needs of maintaining the perfect serving temperatures of wines .
- Thermoelectric and compressor coolers have different temperature capabilities, which can impact the types of wines you can store and serve.
- Choose a cooler that can maintain the precise temperatures required for your favorite wines, ensuring they’re always ready to be enjoyed.
- Compressor coolers offer a wider temperature range, making them more versatile for storing various types of wines.
Let’s take a closer look at the temperature ranges of these two cooling systems.
1. Thermoelectric Cooler Temperature Range
Below is an overview of the temperature range offered by thermoelectric wine coolers:
Temperature Range
- Thermoelectric wine coolers typically have a temperature range that starts around 46°F (8°C) to 66°F (19°C).
- This range is suitable for storing most types of wines, including reds, whites, and rosés.
- However, it’s essential to note that some thermoelectric models may have a narrower temperature range compared to compressor coolers.
Ideal Wine Types
- Thermoelectric coolers are well-suited for storing wines that are best served at slightly cooler temperatures.
- This includes most white wines, rosés, and some lighter red wines.
- While thermoelectric coolers may struggle to reach very low temperatures required for champagne or some dessert wines.
- They excel in maintaining stable temperatures ideal for preserving the flavors and aromas of delicate wines.
Temperature Stability
- One of the key advantages of thermoelectric coolers is their ability to maintain stable temperatures within a narrow range.
- This consistency is essential for ensuring that wines age properly and retain their optimal characteristics over time.
- By providing a stable environment, thermoelectric coolers help wine enthusiasts store their collections effectively.
Considerations
When choosing a thermoelectric wine cooler based on temperature range, consider the types of wines you plan to store.
- If your collection consists mainly of wines that do not require extremely low temperatures, a thermoelectric cooler can be a reliable and energy-efficient choice.
- However, if you need to store a wide variety of wines with different temperature requirements, you may need to assess whether a compressor cooler with a wider temperature range would better suit your needs.
2. Compressor Cooler Temperature Range
The compressor wine coolers offer a wider temperature range compared to thermoelectric models, making them versatile for storing various types of wines. Here is a detailed breakdown:
Temperature Range
- Compressor coolers typically have a broader temperature range that can go as low as 36-40 degree Fahrenheit (around 2-4°C) and 65-68 degree Fahrenheit (around 18-20°C).
- This wide range allows for the storage of different types of wines that require specific temperature conditions for optimal preservation and serving.
Ideal Wine Types
- Due to their wider temperature range capabilities, compressor coolers are suitable for storing a variety of wines, including both reds and whites.
- Whether you prefer a crisp white wine chilled to perfection or a robust red wine kept at a slightly warmer temperature, a compressor cooler can accommodate these preferences effectively.
Temperature Stability
- Compressor coolers excel in providing stable temperature conditions within the cabinet.
- The efficient vapor compression cycle ensures that the set temperature is maintained consistently, which is crucial for proper wine storage.
- This stability helps wines age correctly and retain their flavors and aromas over time.
Considerations
When selecting a compressor wine cooler based on temperature range, consider the specific types of wines you plan to store.
- If your collection includes a variety of wines with different temperature requirements, a compressor cooler is well-suited to meet these diverse needs.
- If you enjoy serving a range of wines at different temperatures, a compressor cooler’s broader range can accommodate these preferences effectively.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
The type of cooling technology used can have a significant energy efficiency impact and operational savings. Let’s take a closer look at the energy efficiency of each option.
1. Thermoelectric Cooler Energy Efficiency
- Thermoelectric coolers have a continuous operation, meaning they are constantly running to maintain the desired temperature.
- While they offer precise temperature control, this continuous operation can lead to higher energy consumption and, subsequently, higher energy bills.
- Additionally, because they are always on, there is a higher chance of potential breakdowns, which can further impact energy efficiency and require maintenance costs.
2. Compressor Cooler Energy Efficiency
Compressor coolers, on the other hand, operate in cycles similar to standard refrigerators.
- They turn on when needed to cool the wine and then cycle off once the desired temperature is reached.
- This cycling helps reduce overall power draw and energy consumption.
- Compressor coolers offer better energy efficiency and can lead to considerable operational savings over time.
- They are particularly advantageous in hot weather conditions. They are designed to handle high ambient temperatures more effectively, ensuring optimal cooling performance even when the outside temperatures rise.
- In contrast, thermoelectric coolers may struggle to cool effectively in such conditions, leading to decreased energy efficiency and potential temperature fluctuations.
3. Energy Efficiency & Unit Size
It is worth noting that the energy efficiency of both thermoelectric and compressor coolers can improve with larger-sized units. Larger wine coolers generally have better insulation and more advanced cooling technologies, resulting in improved energy efficiency overall.
| Thermoelectric Cooler | Compressor Cooler | |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Operation | ✅ | ❌ |
| Cycling Operation | ❌ | ✅ |
| Energy Consumption | Higher | Lower |
| Operational Savings | Less | Higher |
| Performance In Hot Weather | Less Efficient | More Efficient |

Noise And Vibration Comparison
Thermoelectric coolers have a distinct advantage over compressor coolers when comparing the noise levels.
- The absence of moving parts in thermoelectric coolers means they operate almost silently.
- When properly installed on a firm, level surface, these coolers produce no noise whatsoever. This makes them an excellent choice for those seeking a quiet and peaceful wine storage experience.
Compressor coolers, being refrigerators, can generate noise when their compressor is in operation. The compressor is responsible for cooling the cabinet and can produce audible sounds during its cycles.
- While some modern compressor coolers are designed to minimize noise, it’s important to consider this factor if you prefer a more serene environment for your wine collection.
- In addition to noise, the vibrations produced by compressor coolers can potentially disturb the sediments in wine bottles.
- These sediments play a crucial role in the aging and flavor development of wine. Excessive vibration can disrupt this natural process and impact the overall quality of the wine.
- Therefore, if you have a collection of fine wines that require undisturbed aging, a thermoelectric cooler with minimal vibrations may be the better option for you.
Consider the noise and vibration levels when choosing between a thermoelectric and a compressor wine cooler.
- For a quiet and tranquil storage environment that won’t disturb your wine bottles’ sediments, a thermoelectric cooler is the ideal choice.
- If noise isn’t a concern and you prioritize other factors such as temperature range and energy efficiency, a compressor cooler may well be your preferred option.

Environmental Impact
The choice between a thermoelectric cooler and a compressor cooler has significant implications when comparing the environmental impact.
- Compressor coolers use refrigerants, which emit greenhouse gases and contribute to global warming. While modern refrigerants are less harmful than their predecessors, improper disposal can still lead to environmental and health hazards.
- Thermoelectric coolers have no harmful emissions and do not use any hazardous substances. This makes them a more eco-friendly cooling option. These models are easier to dispose of properly, as they do not require complex disposal processes.
Overall, from an environmental perspective, thermoelectric coolers have a lower impact compared to compressor coolers. By choosing a thermoelectric cooler, you can reduce your carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner and healthier planet.
| Environmental Impact | Thermoelectric Cooler | Compressor Cooler |
|---|---|---|
| Refrigerants | No harmful emissions | Emit greenhouse gases |
| Hazardous Waste | No hazardous substances used | Potential environmental and health hazards |
| Disposal | Easier to dispose of properly | Complex disposal processes |
Choosing The Right Wine Cooler
When it comes to selecting the perfect wine cooler, several factors should be considered based on your personal preferences, budget, and the specific needs of your wine collection. Whether you opt for a thermoelectric or compressor wine cooler, it’s essential to evaluate the following criteria:
1. Temperature Range Requirements
- Consider the temperature range that your wine collection requires.
- Thermoelectric coolers typically cannot cool below 46°F, which may impact the storage of sparkling wines.
- In contrast, compressor coolers allow a wider range of wine types and serving preferences.
2. Energy Efficiency
- Analyze the energy efficiency of the wine cooler models you are considering.
- Thermoelectric coolers tend to operate continuously, leading to higher energy bills.
- Compressor coolers cycle on and off, resulting in lower energy consumption and potential cost savings over time.
3. Noise & Vibration Tolerance
- Assess your tolerance for noise and vibration in your wine storage area.
- Thermoelectric coolers operate silently due to the absence of moving parts, while compressor coolers can generate noise when the compressor is running.
- Vibrations from compressor coolers may impact the sediment in your wine bottles, potentially affecting their flavor and aging processes.
4. Environmental Impact
- Consider the environmental impact of your wine cooler choice.
- Compressor coolers utilize refrigerants that can emit greenhouse gases and contribute to global warming.
- Thermoelectric coolers are more eco-friendly and do not involve the use of hazardous substances.
- Proper disposal of refrigerants is crucial to minimize environmental and health hazards.
By carefully assessing your storage needs and considering the advantages and disadvantages of each type of wine cooler, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your personal preferences, budget, and wine collection requirements.

Bottom Line
Overall, consider the advantages and disadvantages of compressor and thermoelectric wine coolers. Take into account factors such as temperature range, energy efficiency, noise and vibration levels, and environmental impact.
- If you require a wider temperature range and reliable cooling performance, a compressor wine cooler might be the best choice for you. These coolers can reach lower temperatures and are better suited for serving a variety of wine types. They also offer superior energy efficiency and can effectively cool in higher ambient temperatures.
- If you prioritize a noise-free operation, vibration-free storage, and an eco-friendly option, a thermoelectric wine cooler could be the right fit. While thermoelectric coolers have a limited temperature range, they are virtually silent, produce no vibrations, and have a smaller environmental footprint.
In the end, it’s all about finding the wine cooling system that aligns with your personal preferences and meets your wine collection’s needs.
Happy cooling!
FoodiesFridge